Fiscal Dominance, Monetary Policy and Exchange Rates: Lessons from Early-Modern Venice
 Fiscal Dominance, Monetary Policy and Exchange Rates: Lessons from Early-Modern Venice
Fiscal Dominance, Monetary Policy and Exchange Rates: Lessons from Early-Modern VeniceAbstract
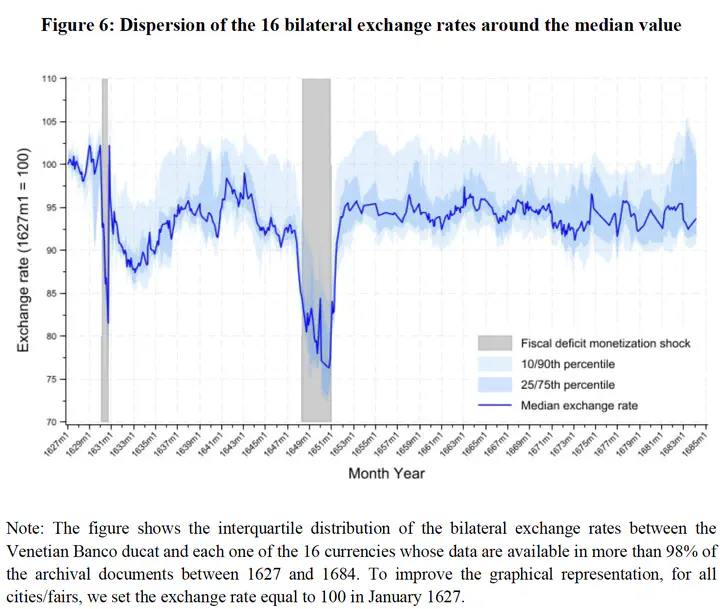
This paper focuses on an early unique experiment of freely floating State-issued money, implemented in Venice between 1619 and 1666. Building on a new hand-collected database from a previously unexplored archival source, we show that, despite the Venetian ducat’s status as an international currency and the government’s reputation for fiscal prudence, its external value was significantly, and increasingly, affected by episodes of automatic government deficit monetization through the Banco del Giro during the crises of 1630 (outbreak of the bubonic plague) and 1648-50 (escalation of the Cretan War). This suggests that the institutional context plays an important role in the transmission mechanism between government deficit monetization and exchange rates.